10 Best Pir Sensors 2025 in the United States
Winner
Philips Hue Outdoor Motion Sensor - Automatic Dusk to Dawn - Turns Lights On When Motion is Detected - 1 Pack - Requires Bridge - Works with Alexa, Google Assistant, and Apple Homekit - Weatherproof
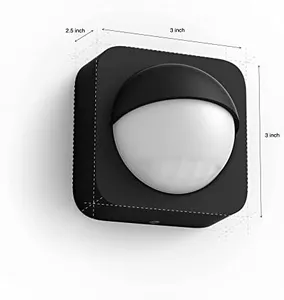
The Philips Hue Outdoor Motion Sensor offers a broad 160-degree detection area, which is quite effective for monitoring large spaces like garages, porches, and backyards. Its maximum range of 40 feet is also sufficient for typical household needs. This sensor is praised for its high sensitivity, turning on the lights immediately when motion is detected, enhancing security and convenience for outdoor areas.
Customer Highlights
A summary of real customer reviews to highlight what shoppers are saying!Customer Highlights
A summary of real customer reviews to highlight what shoppers are saying!Philips Hue Indoor Motion Sensor for Smart Lights (Requires Hue Hub, Installation-Free, Smart Home, Exclusively for Philips Hue Smart Bulbs)
The Philips Hue Indoor Motion Sensor is designed to enhance your smart home lighting with convenience and energy efficiency. It boasts a good detection range suitable for various rooms, such as hallways, bathrooms, and kitchens. The sensor’s field of view is effective for monitoring activity and turning lights on and off accordingly. It's sensitive enough to detect motion quickly, ensuring that lights activate as soon as you enter a room. The device is battery-powered, using 2 AAA batteries (included), making it easy to install without the need for wiring.
Customer Highlights
A summary of real customer reviews to highlight what shoppers are saying!Customer Highlights
A summary of real customer reviews to highlight what shoppers are saying!Top 10 Best Pir Sensors 2025 in the United States
Winner
9.8 score
Philips Hue Outdoor Motion Sensor - Automatic Dusk to Dawn - Turns Lights On When Motion is Detected - 1 Pack - Requires Bridge - Works with Alexa, Google Assistant, and Apple Homekit - Weatherproof
Philips Hue Outdoor Motion Sensor - Automatic Dusk to Dawn - Turns Lights On When Motion is Detected - 1 Pack - Requires Bridge - Works with Alexa, Google Assistant, and Apple Homekit - Weatherproof
Chosen by 1377 this week
Philips Hue Indoor Motion Sensor for Smart Lights (Requires Hue Hub, Installation-Free, Smart Home, Exclusively for Philips Hue Smart Bulbs)
Philips Hue Indoor Motion Sensor for Smart Lights (Requires Hue Hub, Installation-Free, Smart Home, Exclusively for Philips Hue Smart Bulbs)
7.5 score
Philips Hue Indoor Smart Motion Sensor 2022 Version, 2-Pack
Philips Hue Indoor Smart Motion Sensor 2022 Version, 2-Pack
Our technology thoroughly searches through the online shopping world, reviewing hundreds of sites. We then process and analyze this information, updating in real-time to bring you the latest top-rated products. This way, you always get the best and most current options available.