10 Best Gps Chartplotters 2025 in the United States
Winner
Garmin 010-02366-61 GPSMAP 943xsv SideVü, ClearVü and Traditional Chirp Sonar with Mapping - 9", Navionics+
The Garmin 010-02366-61 GPSMAP 943xsv is a robust GPS chartplotter that comes with a 9-inch IPS display, which offers clear and improved display optics for easy readability in various lighting conditions. The screen size is quite generous, making it easy to view maps and sonar details without straining your eyes. This model supports SideVü, ClearVü, and traditional Chirp sonar, providing ultra high-definition scanning to give a detailed view beneath your boat, which is excellent for fishing and navigation.
Customer Highlights
A summary of real customer reviews to highlight what shoppers are saying!Customer Highlights
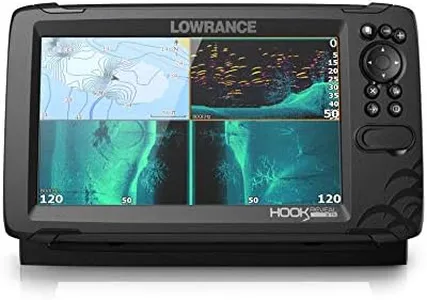
A summary of real customer reviews to highlight what shoppers are saying!Lowrance Eagle Eye 9” Live Sonar with C-MAP US Inland Charts
The Lowrance Eagle Eye 9” Live Sonar is designed for anglers and boaters who want reliable navigation and fish-finding capabilities without the complexity that some other models offer. One of its standout features is the four sonar views it provides, such as Live Forward and DownScan Imaging, allowing for clear images of underwater environments and increased chances of spotting fish. The unit comes with detailed C-MAP charts, which enhance navigation on US inland waters, making it an excellent choice for recreational fishing and boating enthusiasts.
Customer Highlights
A summary of real customer reviews to highlight what shoppers are saying!Customer Highlights
A summary of real customer reviews to highlight what shoppers are saying!Garmin ECHOMAP UHD2 94sv with GT56 Transducer, 9" Touchscreen Chartplotter, Garmin Navionics+ U.S. Coastal
The Garmin ECHOMAP UHD2 94sv is an impressive chartplotter designed for boaters and anglers looking for reliability and advanced features. With its 9-inch touchscreen display, users can expect easy navigation with bright, clear visuals that remain readable even in sunlight. The included GT56-TM transducer provides traditional sonar along with ClearVü and SideVü scanning, ensuring detailed underwater views, which can greatly enhance fishing efficiency. Plus, the built-in Garmin Navionics+ charts cover U.S. coastal areas, offering comprehensive navigation options right out of the box.
Customer Highlights
A summary of real customer reviews to highlight what shoppers are saying!Customer Highlights
A summary of real customer reviews to highlight what shoppers are saying!Top 10 Best Gps Chartplotters 2025 in the United States
Winner
9.9 score
Garmin 010-02366-61 GPSMAP 943xsv SideVü, ClearVü and Traditional Chirp Sonar with Mapping - 9", Navionics+
Garmin 010-02366-61 GPSMAP 943xsv SideVü, ClearVü and Traditional Chirp Sonar with Mapping - 9", Navionics+
Chosen by 1250 this week
Lowrance Eagle Eye 9” Live Sonar with C-MAP US Inland Charts
Lowrance Eagle Eye 9” Live Sonar with C-MAP US Inland Charts
Garmin ECHOMAP UHD2 94sv with GT56 Transducer, 9" Touchscreen Chartplotter, Garmin Navionics+ U.S. Coastal
Garmin ECHOMAP UHD2 94sv with GT56 Transducer, 9" Touchscreen Chartplotter, Garmin Navionics+ U.S. Coastal
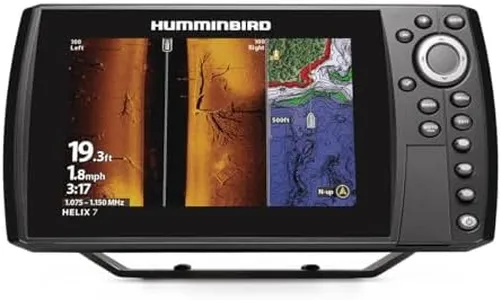
Humminbird 411380-1 Helix 9 Chirp MEGA SI+ GPS G4N Fish Finder
Humminbird 411380-1 Helix 9 Chirp MEGA SI+ GPS G4N Fish Finder
Humminbird 411920-1 Helix 7 SI GPS G4
Humminbird 411920-1 Helix 7 SI GPS G4
Humminbird 411370-1 Helix 9 Chirp MEGA DI+ GPS G4N
Humminbird 411370-1 Helix 9 Chirp MEGA DI+ GPS G4N
Humminbird 411650-1 Helix 7 Chirp MEGA SI GPS G4N
Humminbird 411650-1 Helix 7 Chirp MEGA SI GPS G4N
Garmin ECHOMAP UHD2 74cv with GT20 Transducer
Garmin ECHOMAP UHD2 74cv with GT20 Transducer
8.3 score
Garmin ECHOMAP UHD 73sv, 7" Keyed-Assist Touchscreen Chartplotter with U.S. LakeVü g3
Garmin ECHOMAP UHD 73sv, 7" Keyed-Assist Touchscreen Chartplotter with U.S. LakeVü g3
Our technology thoroughly searches through the online shopping world, reviewing hundreds of sites. We then process and analyze this information, updating in real-time to bring you the latest top-rated products. This way, you always get the best and most current options available.